Present simple forms of ‘to be’: am/is/are
Updated on November 21, 2025
You should learn how to use the present simple forms of “to be” (am, is, are) in English. A1 grammar explanation and interactive exercises that make it easy to learn and get better.
Exercises & Summary
Present simple forms of ‘to be’: am/is/are
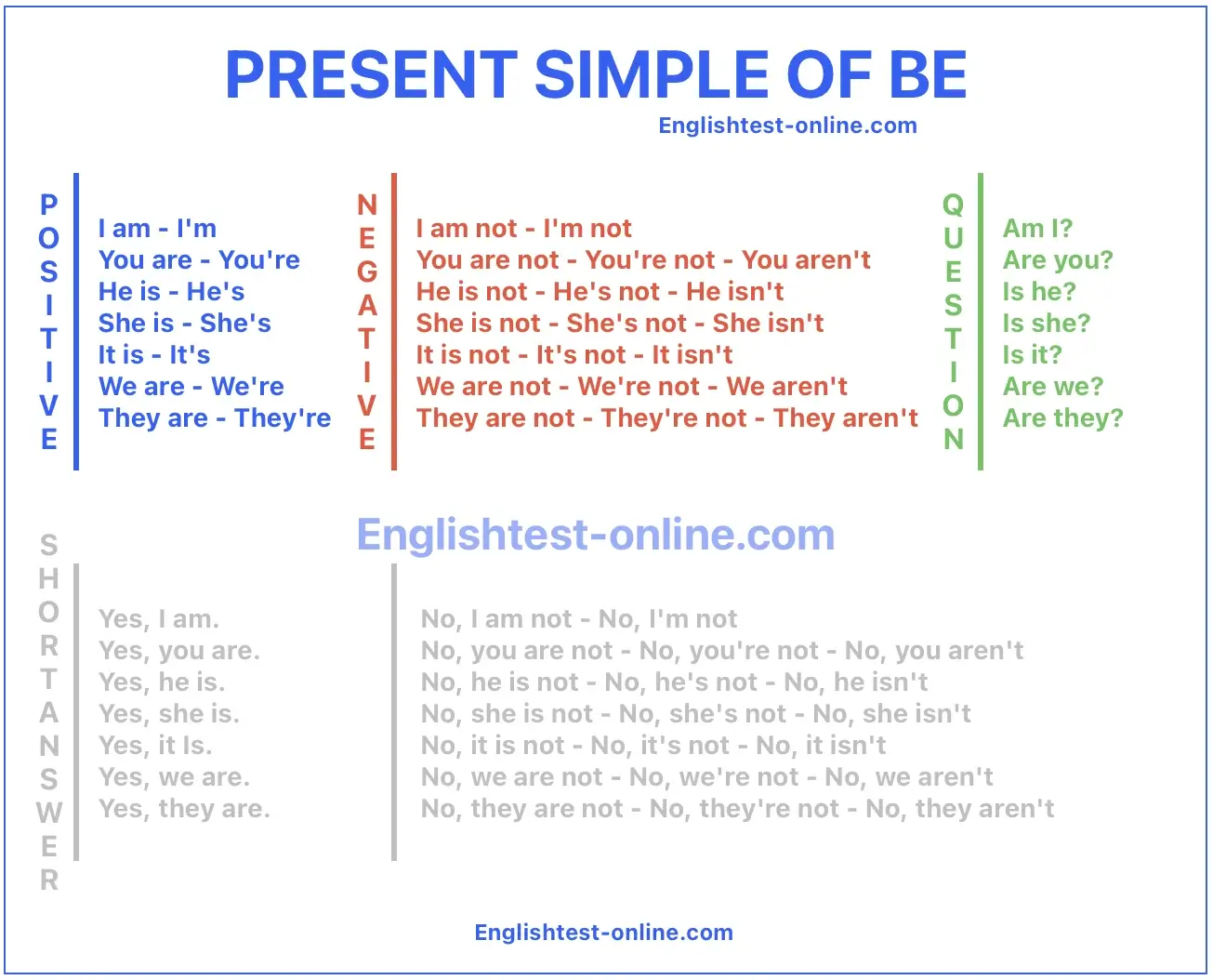
One of the most important verbs in English is “to be.” We use it to talk about where we are, who we are, and how we feel. There are three forms of “to be” in the present simple tense: am, is, and are.
Affirmative (Positive) Form
| Subject | Verb “to be” | Example |
|---|---|---|
| I | am | I am a student. |
| You / We / They | are | You are my friend. / They are at home. |
| He / She / It | is | He is a teacher. / It is cold today. |
Tip: “I” always uses “am,” and “he,” “she,” or “it” always uses “is.”
Negative Form
We add not after the verb to be:
- I am not tired.
- He is not from Spain.
- They are not here.
Short forms (contractions):
- I’m not
- He isn’t / She isn’t / It isn’t
- We aren’t / You aren’t / They aren’t
Question Form
We put the verb to be before the subject:
- Am I late?
- Is he your brother?
- Are they students?
Remember
- “Am” → only with I
- “Is” → with he, she, it (singular)
- “Are” → with you, we, they (plural)
Examples:
- I’m happy today.
- She isn’t at work.
- Are you from Turkey?
The verb “to be” already means “exist,” “stay,” or “feel,” so it doesn’t need another verb in the sentence.
